PYANETI - II. A multidimensional Gaussian process approach to analysing spectroscopic time-series
Abstract
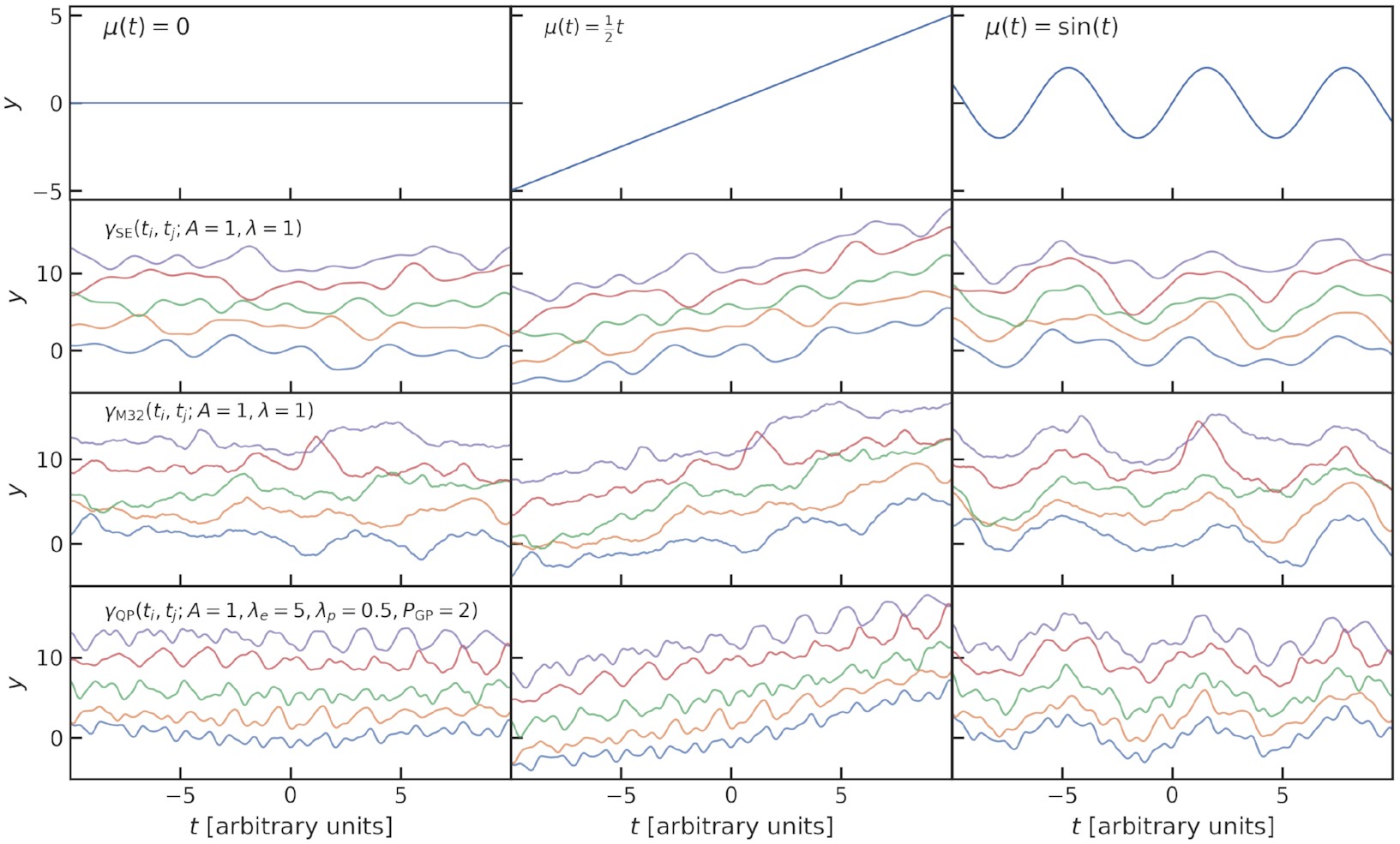
The two most successful methods for exoplanet detection rely on the detection of planetary signals in photometric and radial velocity time-series. This depends on numerical techniques that exploit the synergy between data and theory to estimate planetary, orbital, and/or stellar parameters. In this work, we present a new version of the exoplanet modelling code pyaneti. This new release has a special emphasis on the modelling of stellar signals in radial velocity time-series. The code has a built-in multidimensional Gaussian process approach to modelling radial velocity and activity indicator time-series with different underlying covariance functions. This new version of the code also allows multiband and single transit modelling; it runs on Python 3, and features overall improvements in performance. We describe the new implementation and provide tests to validate the new routines that have direct application to exoplanet detection and characterization. We have made the code public and freely available at https://github.com/oscaribv/pyaneti. We also present the codes citlalicue and citlalatonac that allow one to create synthetic photometric and spectroscopic time-series, respectively, with planetary and stellar-like signals.
- Publication:
-
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
- Pub Date:
- January 2022
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:2109.14086
- Bibcode:
- 2022MNRAS.509..866B
- Keywords:
-
- methods: numerical;
- techniques: photometry;
- techniques: spectroscopy;
- planets and satellites: general;
- Astrophysics - Earth and Planetary Astrophysics;
- Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- This version looks closer to the published one: MNRAS, 509, 866