Progenitors of gravitational wave mergers: binary evolution with the stellar grid-based code COMBINE
Abstract
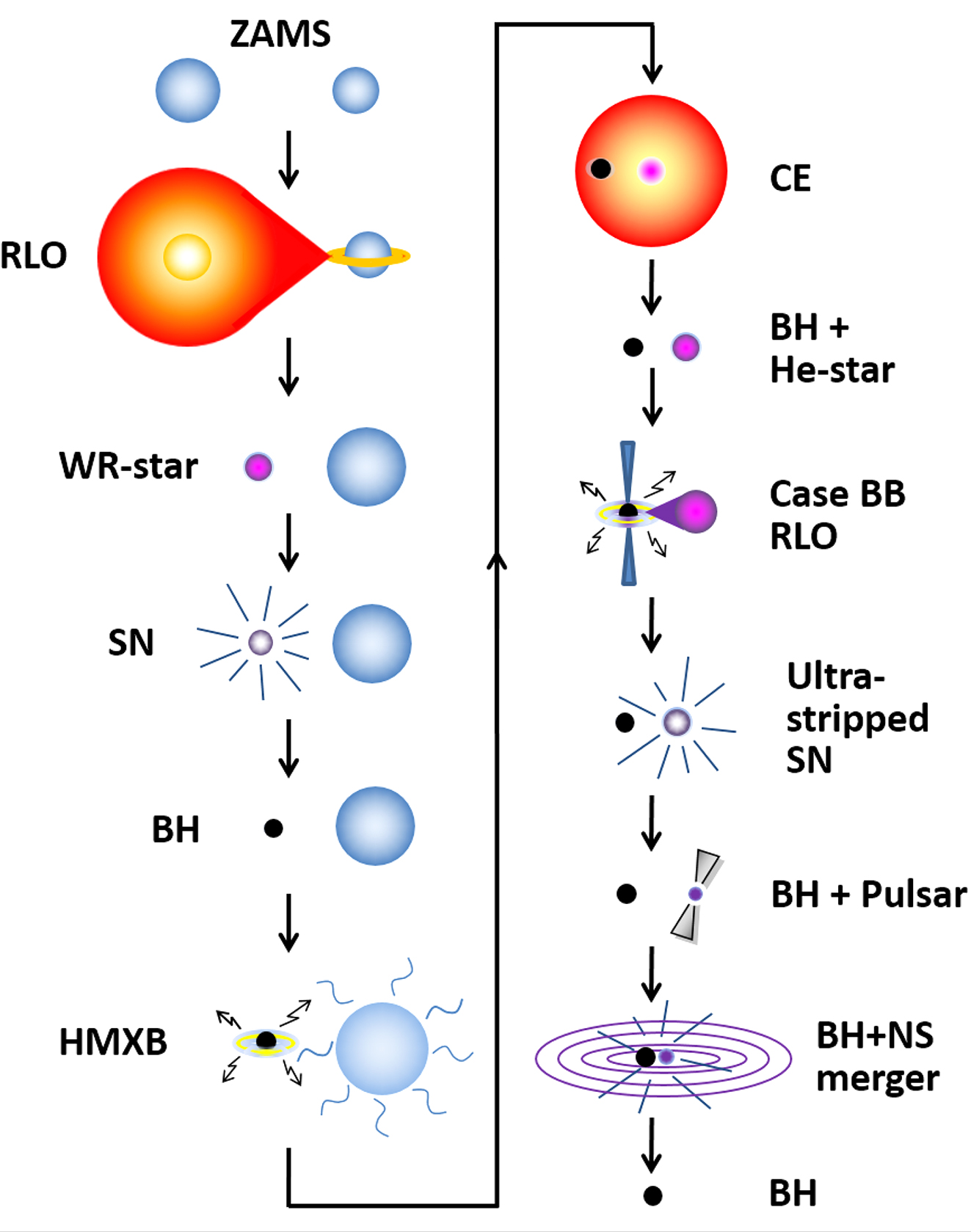
The first gravitational wave detections of mergers between black holes and neutron stars represent a remarkable new regime of high-energy transient astrophysics. The signals observed with LIGO-Virgo detectors come from mergers of extreme physical objects which are the end products of stellar evolution in close binary systems. To better understand their origin and merger rates, we have performed binary population syntheses at different metallicities using the new grid-based binary population synthesis code COMBINE. Starting from newborn pairs of stars, we follow their evolution including mass-loss, mass transfer and accretion, common envelopes, and supernova explosions. We apply the binding energies of common envelopes based on dense grids of detailed stellar structure models, make use of improved investigations of the subsequent Case BB Roche lobe overflow and scale supernova kicks according to the stripping of the exploding stars. We demonstrate that all the double black hole mergers, GW150914, LVT151012, GW151226, GW170104, GW170608, and GW170814, as well as the double neutron star merger GW170817, are accounted for in our models in the appropriate metallicity regime. Our binary interaction parameters are calibrated to match the accurately determined properties of Galactic double neutron star systems, and we discuss their masses and types of supernova origin. Using our default values for the input physics parameters, we find a double neutron star merger rate of {3.0} Myr^{-1} for Milky-Way equivalent galaxies. Our upper limit to the merger-rate density of double neutron stars is R∼eq {400} yr^{-1} Gpc^{-3} in the local Universe (z = 0).
- Publication:
-
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
- Pub Date:
- December 2018
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:1801.05433
- Bibcode:
- 2018MNRAS.481.1908K
- Keywords:
-
- gravitational waves;
- binaries: close;
- stars: evolution;
- gamma-ray burst: general;
- stars: neutron;
- Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics;
- Astrophysics - Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics;
- Astrophysics - High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena
- E-Print:
- 36 pages, 26 figures, 8 tables, plus 9 pages appendix. Accepted 2018 August 6 by MNRAS after revision according to referee report (in particular, including further discussions on the progenitor binary of GW170817)