New ZZ Ceti Stars from the LAMOST Survey
Abstract
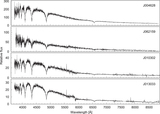
The spectroscopic sky survey carried out by the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) provides the largest stellar spectra library in the world to date. A large number of new DA white dwarfs had been identified based on the LAMOST spectra. The effective temperature ({T}{eff}) and surface gravity ({log}g) of most DA white dwarfs were determined and published in the catalogs. We selected ZZ Ceti candidates from the published catalogs by considering whether their {T}{eff} are situated in the ZZ Ceti instability strip. The follow-up time-series photometric observations for the candidates were performed in 2015 and 2016. Four stars: LAMOST J004628.31+343319.90, LAMOST J062159.49+252335.9, LAMOST J010302.46+433756.2, and LAMOST J013033.90+273757.9 are finally confirmed to be new ZZ Ceti stars. They show dominant peaks with amplitudes rising above the 99.9% confidence level in the amplitude spectra. As LAMOST J004628.31+343319.90 has an estimated mass of ∼0.40 {M}⊙ , and LAMOST J013033.90+273757.9 has a mass of ∼0.45 {M}⊙ derived from their {log}g values, these two stars are inferred to be potential helium-core white dwarfs.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- September 2017
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:1708.07253
- Bibcode:
- 2017ApJ...847...34S
- Keywords:
-
- stars: oscillations;
- surveys;
- white dwarfs;
- Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- 15 pages, 8 figures, 3 tables, accepted for publication in ApJ