X-Ray-powered Macronovae
Abstract
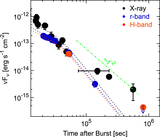
A macronova (or kilonova) was observed as an infrared excess several days after the short gamma-ray burst GRB 130603B. Although the r-process radioactivity is widely discussed as an energy source, it requires a huge mass of ejecta from a neutron star (NS) binary merger. We propose a new model in which the X-ray excess gives rise to the simultaneously observed infrared excess via thermal re-emission, and explore what constraints this would place on the mass and velocity of the ejecta. This X-ray-powered model explains both the X-ray and infrared excesses with a single energy source such as the central engine like a black hole, and allows for a broader parameter region than the previous models, in particular a smaller ejecta mass ∼ {10}-3{--}{10}-2{M}⊙ and higher iron abundance mixed as suggested by general relativistic simulations for typical NS-NS mergers. We also discuss the other macronova candidates in GRB 060614 and GRB 080503, and the implications for the search of electromagnetic counterparts to gravitational waves.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- February 2016
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:1508.05093
- Bibcode:
- 2016ApJ...818..104K
- Keywords:
-
- binaries: general;
- gamma-ray burst: individual: GRB 130603B;
- infrared: stars;
- stars: neutron;
- Astrophysics - High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena
- E-Print:
- 8 pages, 3 figures. Accepted for publication in Astrophysical Journal