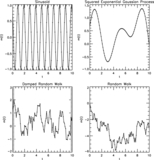
Simulated Performance of Timescale Metrics for Aperiodic Light Curves
Abstract
Aperiodic variability is a characteristic feature of young stars, massive stars, and active galactic nuclei. With the recent proliferation of time-domain surveys, it is increasingly essential to develop methods to quantify and analyze aperiodic variability. We develop three timescale metrics that have been little used in astronomy—Δm-Δt plots, peak-finding, and Gaussian process regression—and present simulations comparing their effectiveness across a range of aperiodic light curve shapes, characteristic timescales, observing cadences, and signal to noise ratios. We find that Gaussian process regression is easily confused by noise and by irregular sampling, even when the model being fit reflects the process underlying the light curve, but that Δm-Δt plots and peak-finding can coarsely characterize timescales across a broad region of parameter space. We make public the software we used for our simulations, both in the spirit of open research and to allow others to carry out analogous simulations for their own observing programs.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- January 2015
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:1410.7882
- Bibcode:
- 2015ApJ...798...89F
- Keywords:
-
- methods: analytical;
- methods: data analysis;
- methods: statistical;
- stars: variables: general;
- techniques: photometric;
- Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics;
- Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics;
- Physics - Data Analysis;
- Statistics and Probability
- E-Print:
- 39 pages, 16 figures, 3 tables. To be published in The Astrophysical Journal. Simulation software is available online at http://ascl.net/1408.012