Detection of Hα Emission in a Methane (T Type) Brown Dwarf
Abstract
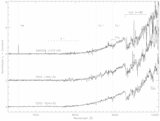
We report the detection of Hα emission in the T dwarf (methane brown dwarf) 2MASSW J1237392+652615 over three days using the Keck Low Resolution Imaging Spectrograph. The measured line flux, log (LHα/Lbol)=-4.3, is roughly consistent with early M dwarf activity levels and inconsistent with decreasing activity trends in late M and L dwarfs. Similar emission is not seen in two other T dwarfs. We speculate on several mechanisms that may be responsible for emission, including a strong magnetic field, continuous flaring, acoustic heat generation, and a close [a~(4-20)RJ] interacting binary, with the cooler component overflowing its Roche lobe. We suggest that the M9.5 Ve PC 0025+0447 could be a warm analog to 2MASS J1237+65 and may be powered by the latter mechanism.
- Publication:
-
The Astronomical Journal
- Pub Date:
- July 2000
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:astro-ph/0003291
- Bibcode:
- 2000AJ....120..473B
- Keywords:
-
- radiation mechanisms: nonthermal;
- Stars: Activity;
- stars: individual (2MASSW J1237392+652615;
- SDSSp J162414.37+002915.6);
- stars: low mass;
- brown dwarfs;
- Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- 14 pages, 3 figures, accepted by AJ