On the CO Near-Infrared Band and the Line-splitting Phenomenon in the Yellow Hypergiant ρ Cassiopeiae
Abstract
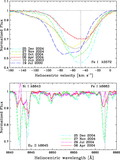
We report on multiepoch optical and near-infrared spectroscopy around the first-overtone rovibrational band of CO in the pulsating yellow hypergiant ρ Cas, one of the most massive stars in the Galaxy and a candidate SN II progenitor. We argue that the double cores of the CO absorption lines, which have previously been attributed to separate circumstellar shells expelled during its recurrent outbursts, result in fact from a superposition of a wide absorption line and a narrow central emission line. The CO line doubling returns over subsequent pulsation cycles, where the superposed line emission assumes its largest intensity near phases of maximum light. We find that the morphology and behavior of the CO band closely resemble the remarkable ``line-splitting phenomenon'' also observed in optical low-excitation atomic lines. Based on radiative transport calculations, we present a simplified model of the near-infrared CO emission emerging from cooler atmospheric layers in the immediate vicinity of the photosphere. We speculate that the kinetic temperature minimum in our model results from a periodic pulsation-driven shock wave. We further discuss a number of alternative explanations for the origin of the ubiquitous emission-line spectrum, possibly due to a quasi-chromosphere or a steady shock wave at the interface of a fast expanding wind and the interstellar medium. We present a number of interesting spectroscopic similarities between ρ Cas and other types of cool variable supergiants, such as the RV Tau and R CrB stars. We further propose a possibly common mechanism for the enigmatic outburst behavior of these luminous pulsating cool stars.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- November 2006
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:astro-ph/0607158
- Bibcode:
- 2006ApJ...651.1130G
- Keywords:
-
- Infrared: Stars;
- Line: Profiles;
- Shock Waves;
- Stars: Atmospheres;
- Stars: Oscillations;
- Stars: Supergiants;
- Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- accepted to ApJ