Distribution of Magnetic Discontinuities in the Solar Wind and in Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence
Abstract
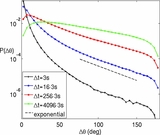
The statistical properties of magnetic discontinuities in the solar wind are investigated by measuring fluctuations in the magnetic field direction, given by the rotation Δθ that the magnetic field vector undergoes during time interval Δt. We show that the probability density function, P(Δθ), can be described by a simple model in which the magnetic field vector purely rotates with a relative increment ΔB/B that is lognormally distributed. We find that the probability density function of increments, P(ΔB/B), has a remarkable scaling property: the normalized variable x = (ΔB/B) · (Δt/Δt 0)-α has a universal lognormal distribution for all time intervals Δt. We then compare measurements from the solar wind with those from direct numerical simulations of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence. We find good agreement for P(Δθ) obtained in the two cases when the magnetic guide field to fluctuations ratio B 0/b rms is chosen accordingly. However, the scale invariance of P(ΔB/B) is broken in the MHD simulations with relatively limited inertial interval, which causes P(Δθ) to scale with measurement interval differently than in the solar wind.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- December 2012
- DOI:
- 10.1088/2041-8205/760/2/L22
- arXiv:
- arXiv:1210.3613
- Bibcode:
- 2012ApJ...760L..22Z
- Keywords:
-
- interplanetary medium;
- magnetohydrodynamics: MHD;
- plasmas;
- solar wind;
- turbulence;
- Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics;
- Nonlinear Sciences - Chaotic Dynamics;
- Physics - Fluid Dynamics;
- Physics - Plasma Physics
- E-Print:
- To appear in Astrophysical Journal Letters