The Ionizing Stars of the Galactic Ultra-Compact H II Region G45.45+0.06
Abstract
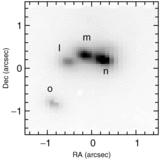
Using the Near-infrared Integral-Field Spectrograph (NIFS) behind the facility adaptive optics module, ALTAIR, on Gemini North, we have identified several massive O-type stars that are responsible for the ionization of the Galactic Ultra-Compact H II region G45.45+0.06. The sources "m" and "n" from the imaging study of Feldt et al. are classified as hot, massive O-type stars based on their K-band spectra. Other bright point sources show red and/or nebular spectra and one appears to have cool-star features that we suggest are due to a young, low-mass pre-main-sequence component. Still two other embedded sources ("k" and "o" from Feldt et al.) exhibit CO bandhead emission that may arise in circumstellar disks which are possibly still accreting. Finally, nebular lines previously identified only in higher excitation planetary nebulae and associated with Kr III and Se IV ions are detected in G45.45+0.6.
- Publication:
-
The Astronomical Journal
- Pub Date:
- May 2008
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:0802.2895
- Bibcode:
- 2008AJ....135.1708B
- Keywords:
-
- dust;
- extinction;
- H II regions;
- infrared: stars;
- instrumentation: adaptive optics;
- stars: formation;
- Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- Latex, 28 pages, 10 figures