The FIRST-2MASS Red Quasar Survey. II. An Anomalously High Fraction of LoBALs in Searches for Dust-Reddened Quasars
Abstract
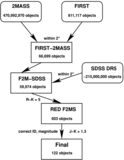
We present results on a survey to find extremely dust-reddened Type 1 quasars. Combining the FIRST radio survey, the 2MASS Infrared Survey and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, we have selected a candidate list of 122 potential red quasars. With more than 80% spectroscopically identified objects, well over 50% are classified as dust-reddened Type 1 quasars, whose reddenings (E(B - V)) range from approximately 0.1 to 1.5 mag. They lie well off the color selection windows usually used to detect quasars and many fall within the stellar locus, which would have made it impossible to find these objects with traditional color selection techniques. The reddenings found are much more consistent with obscuration happening in the host galaxy rather than stemming from the dust torus. We find an unusually high fraction of broad absorption line (BAL) quasars at high redshift, all but one of them belonging to the low-ionization BAL (LoBAL) class and many also showing absorption in the metastable Fe II line (FeLoBAL). The discovery of further examples of dust-reddened LoBAL quasars provides more support for the hypothesis that BAL quasars (at least LoBAL quasars) represent an early stage in the lifetime of the quasar. The fact that we see such a high fraction of BALs could indicate that the quasar is in a young phase in which quasar feedback from the BAL winds is suppressing star formation in the host galaxy.
Based on observations obtained with the W. M. Keck Observatory, which is jointly operated by the California Institute of Technology and the University of California.- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- June 2009
- DOI:
- arXiv:
- arXiv:0808.3668
- Bibcode:
- 2009ApJ...698.1095U
- Keywords:
-
- galaxies: active;
- galaxies: evolution;
- quasars: absorption lines;
- quasars: general;
- Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- 17 pages, 7 figures, accepted for publication in ApJ