A New X-Ray Flare from the Galactic Nucleus Detected with the XMM-Newton Photon Imaging Cameras
Abstract
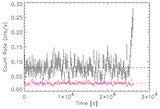
Sgr A*, the compact radio source believed to be the counterpart of the massive black hole at the Galactic nucleus, was observed to undergo rapid and intense flaring activity in X-rays with Chandra in 2000 October. We report here the detection with XMM-Newton European Photon Imaging Cameras of the early phase of a similar X-ray flare from this source, which occurred on 2001 September 4. The source 2-10 keV luminosity increased by a factor of ~20 to reach a level of 4×1034 ergs s-1 in a time interval of about 900 s, just before the end of the observation. The data indicate that the source spectrum was hard during the flare. This XMM-Newton observation confirms the results obtained by Chandra and suggests that in Sgr A* rapid and intense X-ray flaring is not a rare event. This can constrain the emission mechanism models proposed for this source and also implies that the crucial multiwavelength observation programs planned to explore the behavior of the radio/submillimeter and hard X-ray/gamma-ray emissions during the X-ray flares have a good chance of success.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- February 2003
- DOI:
- 10.1086/345749
- arXiv:
- arXiv:astro-ph/0207620
- Bibcode:
- 2003ApJ...584..751G
- Keywords:
-
- Accretion;
- Accretion Disks;
- Black Hole Physics;
- Galaxy: Center;
- X-Rays: General;
- Astrophysics
- E-Print:
- 18 pages, 6 color figures, final version, accepted on October 24, 2002, to appear in ApJ, v584 n2 ApJ February 20, 2003 issue